Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) have become integral to modern medical technology. Their ability to offer immersive, real-time visualization and simulation has opened new frontiers for surgeons, clinical education, and patient care. Both AR and VR promise to revolutionize the healthcare industry, providing tools that enhance precision and improve healthcare services.
Overview of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Applications in Healthcare
Several key factors explain why augmented reality and virtual reality are generating interest within the medical field:
Enhanced Visualization: AR overlays 3D images onto medical images, providing surgeons with precise information during surgical procedures. This use of augmented reality enhances precision and minimizes risks.
Immersive Patient Rehabilitation: VR creates virtual environments for rehabilitation. This is particularly useful for neurological therapy, where patients can practice movements in a safe space.
Medical Training Simulations: AR and VR simulate complex medical procedures for medical students and healthcare professionals, enabling them to gain practical experience without risks.
Real-Time Remote Collaboration: With augmented reality-based telementoring, experts can guide health workers remotely during critical surgical procedures using real-time feedback.
Cost Reduction: Implementing AR and VR can reduce the need for physical medical devices in training, cutting costs while maintaining high-quality education and training experiences.
The Significance of VR and AR in Healthcare Today
AR and VR play a pivotal role in modern healthcare, offering solutions for patient care, education, and therapy. Below are key examples of how AR and VR are currently applied in the healthcare industry.
Use of AR for Surgical Guidance
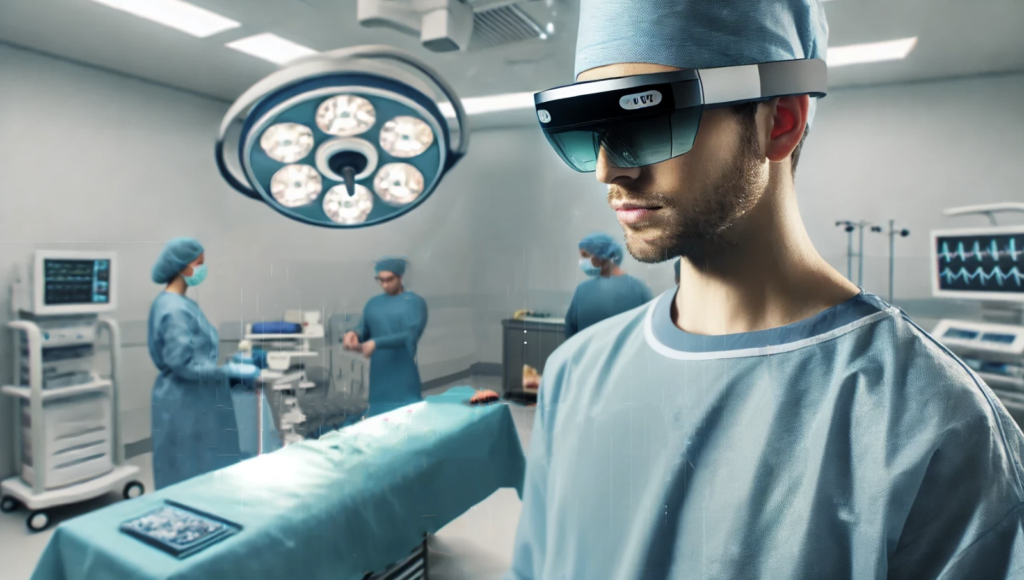

AR technology offers critical support during surgical procedures. It provides real-time overlays of medical images onto a surgeon’s field of view, improving accuracy during delicate operations. A study published in Spine [1] highlights the benefits of augmented reality in spine surgery. This systematic review found that AR navigation significantly improves surgical precision and reduces the risk of complications. The application of augmented reality allows surgeons to visualize virtual objects like bones and nerves over the patient’s anatomy, enabling safer and more efficient procedures. Using augmented reality ensures that surgeons can perform with enhanced visibility, making it a vital technology in healthcare.
VR for Patient Therapy and Rehabilitation
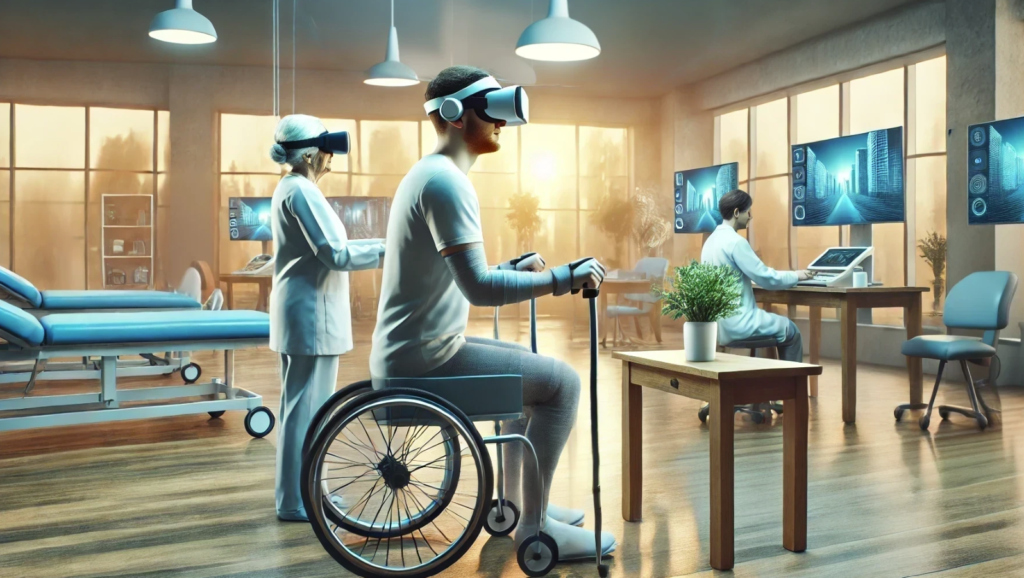

VR has proven to be an effective tool in rehabilitation and patient therapy, particularly for neurological conditions. According to a study published in Brain Sciences [2], VR creates immersive environments that help patients recover motor skills and cognitive functions by simulating real-world activities. This virtual environment is beneficial for patients with limited mobility, as it allows them to practice movements safely and engage in interactive exercises that would be difficult to perform in physical settings. The use of VR also aids in reducing anxiety and pain during rehabilitation sessions, offering patients a distraction from discomfort and creating a more engaging therapeutic process.
AR and VR in Medical Skills Training and Simulation
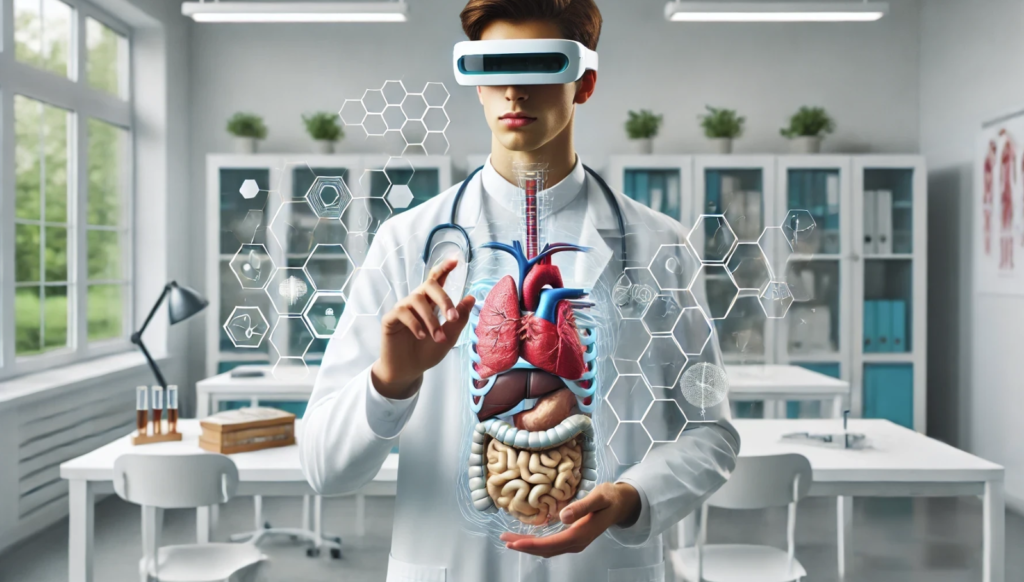

Augmented and virtual reality have transformed medical training, offering simulation-based learning that bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. A study in the Journal of Medical Education [3] highlights how AR and VR provide a possibility to train medical students and health professionals with interactive virtual experiences. These tools allow medical practitioners to practice procedures and interact with virtual patients in a virtual world, simulating various health conditions without risking patient safety. AR technology enhances understanding by overlaying digital imaging onto anatomical models, while VR offers full simulations of complex medical scenarios, making it easier for healthcare providers to master critical skills. This training tool is invaluable in preparing professionals for real-world challenges.
The Future Impact of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The future of virtual reality and augmented reality in medicine holds both challenges and promising opportunities:
Integration and Accessibility: Widespread adoption of AR and VR requires affordable solutions that can be easily integrated into existing healthcare services. Developing user-friendly platforms will be key to success.
Ethical Considerations: As reality technology evolves, ethical concerns about patient privacy and data security become increasingly significant. It is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure compliance with regulations.
Enhanced Remote Care: The use of AR for telementoring and VR for virtual care could address gaps in rural healthcare access, enabling healthcare professionals and providers to assist patients remotely.
Continuous Technological Advancements: The capabilities of virtual and augmented reality are constantly improving, with augmented reality applications becoming more accurate and virtual reality offering more realistic simulations. This means more opportunities for professionals to adopt these tools for better patient outcomes.
Research and Development: Further systematic reviews and meta-analyses will help refine these technologies, ensuring they align with clinical needs and provide evidence-based solutions for patient care.
Contact Us for Integrating AI in Your Healthcare Solutions
For expert advice on integrating AI and augmented reality into your healthcare services, contact Neural Board. We are here to guide you in choosing the best technology for your organization’s needs.
References
- Felix, Brent, et al. “Augmented reality spine surgery navigation: increasing pedicle screw insertion accuracy for both open and minimally invasive spine surgeries.” Spine 47.12 (2022): 865-872.
- Rodriguez-Hernandez, Marta, et al. “Effects of specific virtual reality-based therapy for the rehabilitation of the upper limb motor function post-ictus: randomized controlled trial.” Brain Sciences 11.5 (2021): 555.
- Dhar, Poshmaal, et al. “Augmented reality in medical education: students’ experiences and learning outcomes.” Medical education online 26.1 (2021): 1953953.
Q: How is augmented reality technology applied to medical devices?
A: Augmented reality technology is integrated into medical devices to provide real-time data visualization, enhance surgical precision, and improve training for healthcare professionals. This integration helps in the effective use of AR in medical environments.
Q: What is the role of mixed reality in healthcare?
A: Mixed reality combines elements of both augmented and virtual reality to create immersive environments for training, surgical planning, and real-time collaboration among healthcare professionals. This approach enhances the use of AR and VR in medical applications.
Q: Can you explain the benefits of AR in patient education?
A: The benefits of AR in patient education include improved understanding of medical procedures, enhanced visualization of anatomy, and the ability to simulate treatment options. This technology can make complex information more accessible and engaging for patients.
Q: How does reality for healthcare change the way healthcare is delivered?
A: Reality for healthcare transforms delivery by offering immersive training for professionals, enhancing patient experiences, and enabling more precise surgical interventions. This shift improves outcomes and streamlines healthcare processes.
Q: What are the challenges in implementing AR in healthcare settings?
A: Challenges include the need for high-quality AR content, integration with existing medical devices, ensuring user-friendliness, and addressing regulatory concerns. Overcoming these barriers is essential for the successful use of AR and VR in healthcare.